News
How do we identify thyroid problems?
21.4.2023
Rapid, unexplained weight gain or loss is one of the common symptoms of thyroid dysfunction.
The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland, which means that it secretes hormones into the blood, from where they pass into the body's tissues. It is shaped like a butterfly and is located at the front of the neck, below the largest cartilage of the throat, the thyroid cartilage. It secretes the hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine, which control the rate of metabolism. It happens that the thyroid gland secretes too few or, more rarely, too many hormones, thereby causing a slowdown in metabolism or its excessive activity.
Rapid, unexplained weight gain or loss is one of the common symptoms of thyroid dysfunction. If the thyroid gland is underactive and secretes too few hormones, we gain weight. This condition is called hypothyroidism. Conversely, an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism) causes unexpected weight loss.
Increased appetite and weight loss at the same time
Thyroid hormones affect heart rate. People with an underactive thyroid notice that their heart beats slower than normal. Reduced activity of the thyroid gland also affects circulation by reducing the elasticity of blood vessels and thus raising blood pressure. Increased thyroid activity causes a fast heartbeat and feelings of "heart pounding", but it can also cause abnormal heart rhythms. Too little secretion of thyroid hormone can also result in high blood pressure.
Abnormal heart rhythms
Too little or too much secretion of thyroid hormones significantly affects mood and life energy. The result of insufficient thyroid secretion is constant fatigue, lack of interest, lack of motivation, sadness, depression. Excessive secretion of thyroid hormones causes emotional imbalance, irritability, restlessness, sleep problems, as well as increased appetite.
Mood swings
Changes in the secretion of thyroid hormones affect the menstrual cycle. Symptoms are similar to menopause: absence of menstruation, decreased libido, increased irritability, forgetfulness, depressed feelings, unusual weight changes, fatigue and hair loss. Based on blood tests, we determine whether the problems are related to menopause or thyroid hormones. It can be a combination of both, because thyroid function is directly and indirectly also dependent on estrogen, and thyroid dysfunction is more common when transitioning to menopause (or during puberty).
Hair loss
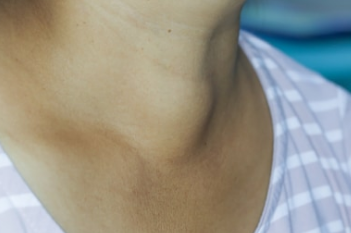
Swelling in the neck can be a sign that something is wrong with the thyroid gland. An enlargement of the thyroid gland is called a goiter. The most common cause of goiter is a lack of iodine in food. With a lack of iodine, growth factors are secreted, which cause the growth of cells in the thyroid gland and its subsequent increase. Even with a sufficiently large intake of iodine in the body, goiter can occur. It can be the result of hereditary disorders in the formation and metabolism of thyroid hormones, Graves' disease, the presence of certain drugs in food, increased production of a hormone that stimulates the secretion of thyroid hormones, a thyroid tumor... Hormone secretion can be normal, increased or decreased in goiter. Symptoms that may occur with a large goiter are difficulty breathing, feeling of a foreign body in the throat, hoarseness, cough, difficulty swallowing, swelling in the lower part of the neck.
If abnormal thyroid function is suspected, blood tests should be performed to determine the levels of the TSH hormone, which regulates the functioning of the thyroid gland and thyroid hormones.
It is recommended that you bring blood tests with you to your thyroid ultrasound. Using ultrasound, we obtain information on the size, structure and blood supply of this gland, detect various formations and cysts, and assess their importance. An ultrasound can be used to suspect inflammation of the thyroid gland.
For questions we are available via telephone 041 347 444, via e-mail info@ultralab.si or simply fill out the form below.
This is a private practise.